 |
usa | world | animals | vocabulary | health | science | math | history |
Gabon Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
Several Bantu groups occupied the area that is now Gabon when France occupied it in 1885. In 1910, Gabon became one of the four territories of French Equatorial Africa, a federation that survived until 1959. These territories became independent on August 17, 1960. The first president of Gabon, elected in 1961, was Léon M’ba, with Omar Bongo as his vice president. When M'Ba died in 1967, Bongo replaced him as president, and has been the head of state ever since and also won re-election.
|
||||
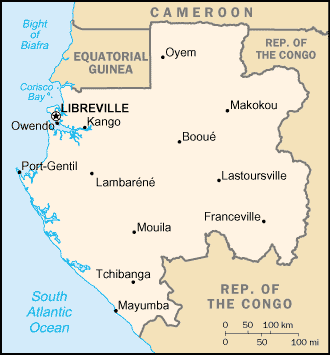 The Gabonese Republic, or Gabon, is a nation of west central Africa. It borders on Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo and the Gulf of Guinea. Ruled by autocratic presidents since independence from France on August 17, 1960, Gabon introduced a multiparty system and a new constitution in the early 1990s that allowed for a more transparent electoral process and for reforms of governmental institutions. A small population, abundant natural resources, and foreign private investment have helped make Gabon one of the more prosperous countries in the region.
The Gabonese Republic, or Gabon, is a nation of west central Africa. It borders on Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo and the Gulf of Guinea. Ruled by autocratic presidents since independence from France on August 17, 1960, Gabon introduced a multiparty system and a new constitution in the early 1990s that allowed for a more transparent electoral process and for reforms of governmental institutions. A small population, abundant natural resources, and foreign private investment have helped make Gabon one of the more prosperous countries in the region.