 |
usa | world | animals | vocabulary | health | science | math | history |
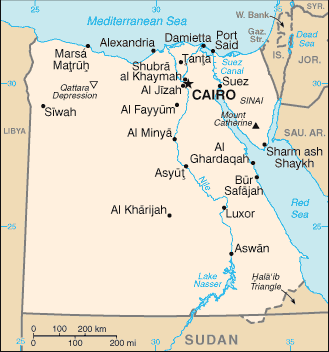
Egypt
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
Covering an area of about 1,020,000 km² Egypt includes the Sinai Peninsula (considered part of Southwest Asia), while the majority of the country is located in North Africa. It shares land borders with Libya to the west, Sudan to the south, and Israel to the northeast. It is bordered to the north and east by the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, respectively. The vast majority of Egypt's population inhabits the banks of the River Nile (about 40,000 km²). Large areas of land are part of the Sahara Desert and are sparsely inhabited. Egypt is famous for its ancient civilization and some of the world's most stunning ancient monuments, including the Giza Pyramids, the Karnak Temple and the Valley of the Kings; the southern city of Luxor contains a particularly large number of ancient artifacts. Today, Egypt is widely regarded as the main political and cultural centre of the Arab and Middle Eastern regions. Mir, the Arabic and official name for Egypt, is of Semitic origin, and possibly means 'a country' or 'a state'. The name Egypt came via the Latin word Aegyptus derived from the ancient Greek word Αίγυπτος "aiguptos", which in turn is derived from the ancient Egyptian phrase"Hut ka Ptah", the name of a temple of the god Ptah at Memphis. For details see the article Copt. The regularity and richness of the annual Nile River flood, coupled with semi-isolation provided by deserts to the east and west, allowed for the development of one of the world's great civilizations. A unified kingdom was founded circa 3200 BC by King Menes, and a series of dynasties ruled in Egypt for the next three millennia. The last native dynasty, known as the Thirtieth Dynasty, fell to the Persians in 341 BC who dug the predecessor of the Suez canal and connected the Red Sea to the Mediterranean. Later, Egypt fell to the Greeks, Romans, Byzantines and Persians again. It was the Muslim Arabs who introduced Islam and the Arabic language in the seventh century changing Egypt into a linguistically "Arab" nation once and for all. Muslim rulers nominated by the Islamic Caliphate remained in control of Egypt for the next six centuries. A local military caste, the Mamluks took control about 1250 and continued to govern even after the conquest of Egypt by the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, Egypt became an important world transportation hub; however, the country also fell heavily into debt. Ostensibly to protect its investments, Britain seized control of Egypt's government in 1882, but nominal allegiance to the Ottoman Empire continued until 1914. Partially independent from the UK in 1922, Egypt acquired full sovereignty following World War II. Between 1924-1936 there existed a short-lived attempt to model Egypt's constitutional government after the European style of government; this was called Egypt's Liberal Experiment. In 1952 a popularly-supported military coup d'état forced King Farouk I, a constitutional monarch, to abdicate in support of his son King Ahmed Fouad II. Finally the Egyptian Republic was declared on 18 June 1953 with Gen. Mohamed Naguib as the first President of the Republic. After Naguib resigned in 1954, Gamal Abdel Nasser, the real architect of the 1952 Revolution, assumed power as President and nationalized the Suez Canal leading to the 1956 Suez Crisis. Between 1958 and 1961 Egypt and Syria formed a union known as the United Arab Republic.
This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Egypt". |
 The Arab Republic of Egypt, commonly known as Egypt is a republic mostly located in North-Eastern Africa.
The Arab Republic of Egypt, commonly known as Egypt is a republic mostly located in North-Eastern Africa.